5G(二)5G 网络架构 -- 1. 核心网架构
一、5G 不同应用场景的需求指标差异
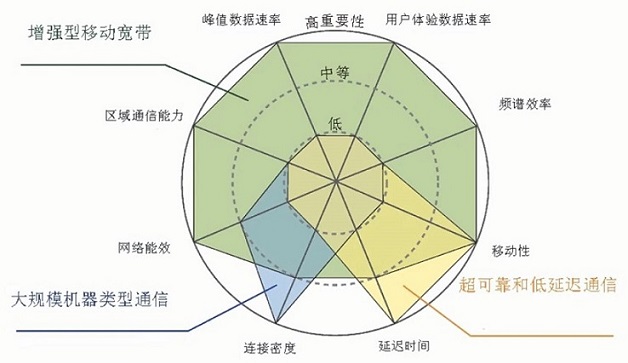
有时不同场景所需的性能是不同的,甚至是矛盾的,单一网络没办法满足需要(4G 网络就是单一网络)
那 5G 网络是如何解决这个问题?
建立三个网络:5G eMBB、5G uRLLC、5G mMTC,但是成本太高,而且网络会非常复杂
二、5G 时代的网络挑战和改进方向
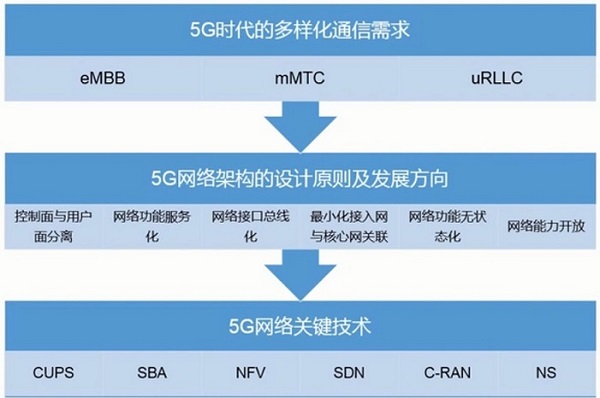
发展方向
解决方法:使用网络切片,分层三种网络,但不是物理层面,而是网络层面
1. 控制面和用户面分离
ex: 要增加用户数量,升级的是控制面;要提升传输速率,升级的是用户面。
在 4G 网络核心网中已经完成了一部分的分离,主要控制面在 MME,用户面在 S-GW 和 P-GW,但在 S-GW 和 P-GW 中仍含有会话控制相关的控制功能(例如 IP 地址分配),分离的不彻底。唯有网络更加灵活,才可能完成网络切片。
补充:MME 是 LTE 网络的网元,和 S-GW、P-GW 一起被称作 4G 的核心网:EPC。
这三个网元都是逻辑网元,意味着任何厂家(爱立信,华为,中兴等)建立的 LTE 网络必须要有这三个逻辑网元。
实际生产过程中,为了节省成本,有些技术好的厂家可以用一套系统(硬件 + 软件)同时作为 3G 网元和 4G 网元,
比如华为经常把 3G 的 SGSN 和 4G 的 MME 共用一套系统(硬件 + 软件),
华为的 S-GW,P-GW 经常合一为一套系统,同时还支持 3G 的 GGSN。
2. 网络功能服务化
软硬件解耦,在更新的时候,可以只更新软件而硬件不更新。
网络功能服务化,5G 中没有网元的概念,网络单元(Net Element,简称 NE,网元)。
3. 网络接口总线化
5G 中,任何一个网络功能都可以给其他网络功能提供服务,也可以从其他网络功能得到服务。
而在 4G 中,强调的是网元之间的接口。
4. 最小化核心网和接入网的关联
目标:不论接入网是是什么 (3G、4G、5G…) 都可以接入到 5G 的核心网中。
5. 网络功能无状态化
在 4G 中有些网元既要控制又要存储。
在 5G 中控制和存储分别是专门的网络功能。
6. 网络能力开放
运营商不甘心成为管道化的工具,
可以给某些特定的用户提供定制化的服务。
关键技术(用哪些关键技术来实现上述目标)
1.CUPS(控制和用户分离)
该技术引入 4G 网中,让用户提前体会到 5G 的性能。
2.SBA(基于服务的网路架构)
用来满足网络功能服务化
3.NFV(网络功能虚拟化)
4.SDN
满足网络功能服务化、控制面和用户面分离
5.C-RAN(5G 中新形式的接入网)
6.NS(网络切片)
三、5G 网络结构
5G 网络的总体结构
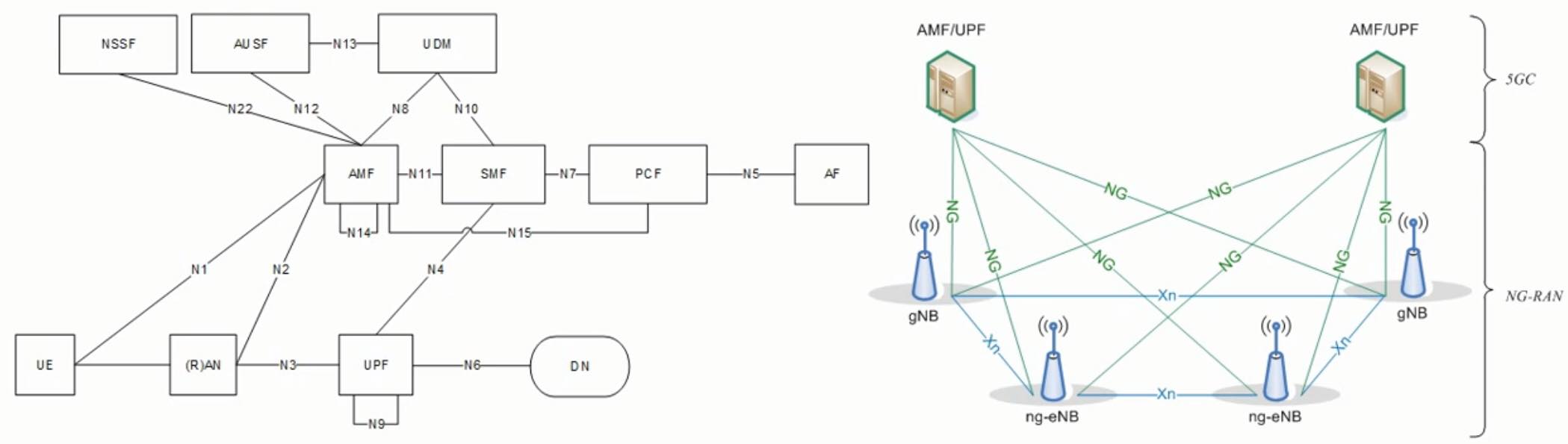
5G 核心网架构(基于服务的结构 SBA)
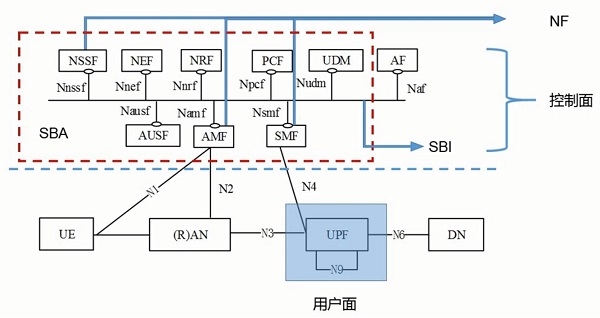 NF:网路服务,而不是 4G 网中的网元
NF:网路服务,而不是 4G 网中的网元
SBI:服务接口
SBA:5G 核心网架构
AF:应用服务器不算 5G 核心网中的一部分
5G 核心网网络功能
1.AMF
类似 4G MME 的功能
Access and Mobility Management function (AMF).
(1) Termination of RAN CP interface (N2).
(2) Termination of NAS (N1), NAS ciphering and integrity protection.
(3) Registration management.
(4) Connection management.
(6) Reachability management.
(6) Mobility management.
(7) Provide transport for SM messages between UE and SMF.
(8) Access Authentication.
(9) Access Authorization.
2.SMF
类似 4G PG-W 的控制面
The Session Management function (SMF)
(1) Session management e.g. Session Establishment, modify and release, including tunnel maintain between UPF and AN node.
(2) UE IP address allocation & management (including optional Authorization).
(3) Selection and control of UP function.
(4) Configures traffic steering at UPF to route traffic to proper destination.
(5) Termination of interfaces towards Policy control functions (PCF).
(6) Termination of SM parts of NAS messages.
3.UPF
The User plane function (UPF).
(1) External PDU session point of interconnect to Data Network.
终端的数据传到外部网络,外部网络的数据传回终端
(2) Packet routing & forwording (e.g. support of Uplink classifier to route traffic flows to an instance of a data network, support muti-homed PDU Session).
(3) User Plane part of policy rule enforcement (e.g. Gating, Redirection, Traffic steering).
(4) QoS handling for user plane, e.g. UL/DL rate enforcement, Reflective QoS marking in DL.
4.PCF
类似 LTE 的 PCRF (Policy and Charging Rules Function),执行统一的策略框架
The Policy Control Function (PCF)
(1) Supports unified policy framework to govern network behaviour.
(2) Provides policy rules to Control Plane functions to enforce them.
(3) Accesses subscription in a Unified Data Rspository (UDR).
访问用户数据库
5.NEF
5G 网络中的新功能,关于网络开放
The Network Exposure Function (NEF)
(1) Exposure of capabilities and events.
(2) Secure provision of information from external application to 3GPP network.
(3) Translation of internal-external information.
(4) The Network Exposure Function receives information from other network functions (base on exposured capablities of other network functions). NEF stores the received information as interface to a Unified Data Repository (UDR). The stored information can be accessed and “re-exposed” by the NEF to other network functions and Application Functions, and used for other purposes such as analytics.
6.NRF
为 SBA 服务的网络功能
The Network Repository Function (NRF)
(1) Supports service discovery function. Receive NF Discovery Request from NF instance, and provides the information of the discovered NF instances (be discovered) to the NF instance.
每个网络功能都是服务化的,要取得服务,要先联系到它,才能请求服务。
NRF 是网络功能互相通信的基础。
(2) Maintains the NF profile of availble NF instances and their supported services.
7.UDM
类似 4G 中的 HSS (包含管理和数据存储) 中的控制功能
The Unified Data Management (UDM)
(1) Generation of 3GPP AKA Authentication Credentials.
(2) User Identification Handling (e.g. storage and management of SUPI for each subscriber in the 5G system).
(3) Support of de-condelment of privacy-protected subcription identifier (SUCI).
(4) Access authorization based on subscriptiondata (e.g. roaming restrictions).
(5) UE’s Serving NF Registration Management (e.g. storing serving AMF for UE, storing serving SMF for UE’s PDU Session).
(6) Subscription management.
8.AUSF
健全服务器功能
The Authrntication Server Function (AUSF)
(1) Supports authentication for 3GPP access and untrusted non-3GPP access.
9.AF
The Application Function (AF)
(1) Application influence on traffic routing.
(2) Accessing Network Exposure Function.
(3) Interacting with the Policy framework for policy control.
9.UDR
相当于 4G 中 HSS 的数据存储功能,统一存放数据的地方。
The Unified Data Repository (UDR)
(1) Storage and retrieval of subscription data by the UDM.
(2) Storage and retrieval of policy data by the PCF.
(3) Storage and retrieval of structured data for exposure.
(4) Application data (including Packet Flow Descriptios (PFDs) for application detection, AF request information for multiple UEs), by the NEF.
10.UDSF
UDR 存储的是结构化数据 (3GPP 定义好的),
UDSF 存储的是非结构化数据 (可能是某个应用自己定义的)
The Unstructured Data Storage Function (UDSF)
(1) Storage and retrieval of information as unstructured data by any NF.
11.SMSF
信息管理,收发短信
The Short Message Service Function (SMSF)
(1) SMS management subscription data checking and conduction SMS delivery accordingly.
(2) SM-RP/SM-CP with the UE.
(3) Relay the SM with the UE.
(4) Relay the SM from SMS-GMSC/WMSC/SMS-Router toward the UE.
(5) Interaction with AMF and SMS- for notification procedure that the UE is unavaliable for SMS transfer (i.e, notifies SMS-GMSC to inform UDM when UE is unavailble for SMS).
12.NSSF
是 5G 中比较重要的功能
The Network Slice Selection Function (NSSF)
(1) Selecting the set of Network Slice instances serving the UE.
(2) Determining the Allowed NSSAI and, if needed, the mapping to hte Subscribed S-NSSAIs.
(3) Determining the Configured NSSAI and, if needed, the mapping to Subscribed S-NSSAIs.
(4) Determining the AMF Set to be used to serve the UE, or based on configuration, a list of candidate AMFs, possibly by querting the NRF.
13.5G-EIR
5G ID 认证中心,检查设备的状态
The 5G-Equipment Identity Register (5G-EIR)
Check the status of PEI (e.g. to check that it has not benn blackkisted)
14.LMF
定位相关的功能,通过上下行的测量得到.. 的位置
The Location Management Function (LMF)
(1) Supports location determination for a UE.
(2) Obtains downlink location measurements a location estimate from the UE.
(3) Obtains uplink location measurements from the NG RAN.
(4) Obtains non-UE associated assistence data from the NG RAN.
15.SEPP
防火墙作用,过滤网络的数据包
The Security Edge Protection Proxy (SEPP)
(1) Message filtering and policing on inter-PLMN control plane interfaces.
(2) Topology hiding.
16.NWDAF
基于切片的网络数据分析
The Network Data Analytics Function (NWDAF)
(1) Represents operator managed network analytics logical function.
(2) Provides slice specific network data analytics to a NF.
(3) Provides network analytics information (i.e., load level information) to a NF on a network slice instance level and the NWDAF is not required to be aware of current subscribers using the slice.
(4) Notifies slice specific network status analytic information to the NFs that are subscribed to it.
(5) NF may collect directly slice specific network status analytic information from NWDAF.This information is not about specific.
四、5G 核心网网络功能服务框架
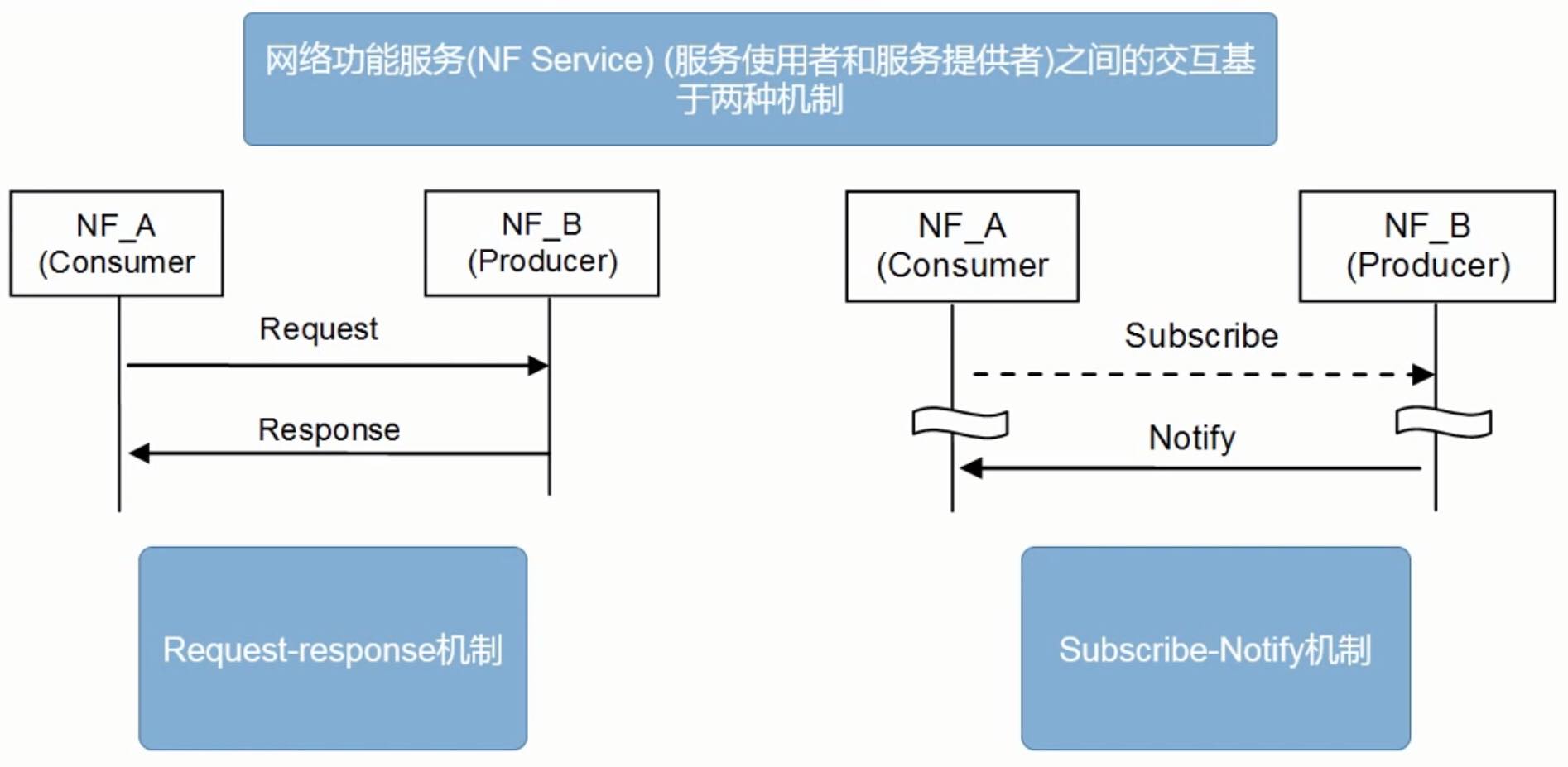
类似用户看视频,可以点击视频观看,也可以订阅 up 主之后会收到通知
网络功能服务 (NF) 的注册、发现、授权机制
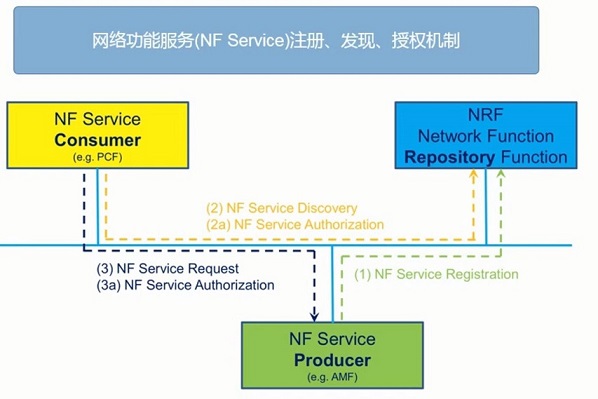
服务 NF 上下之后,向 NRF 发送注册消息,NEF 会存储 NF 的服务状态信息
SBI 接口协议
3G 和 4G 网络核心网的不同网元使用的协议是不一样的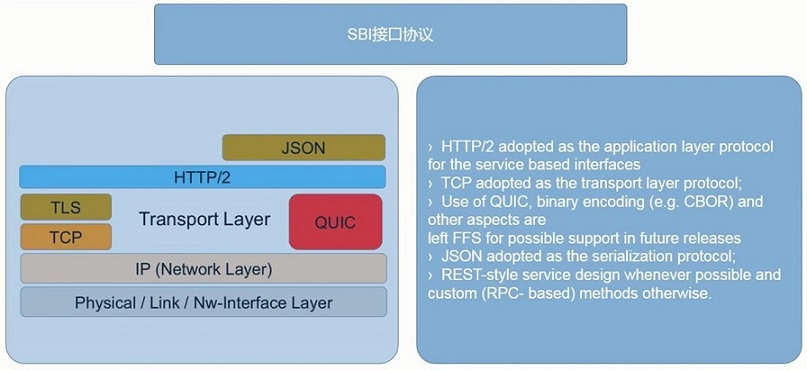
网络服务功能举例:AMF
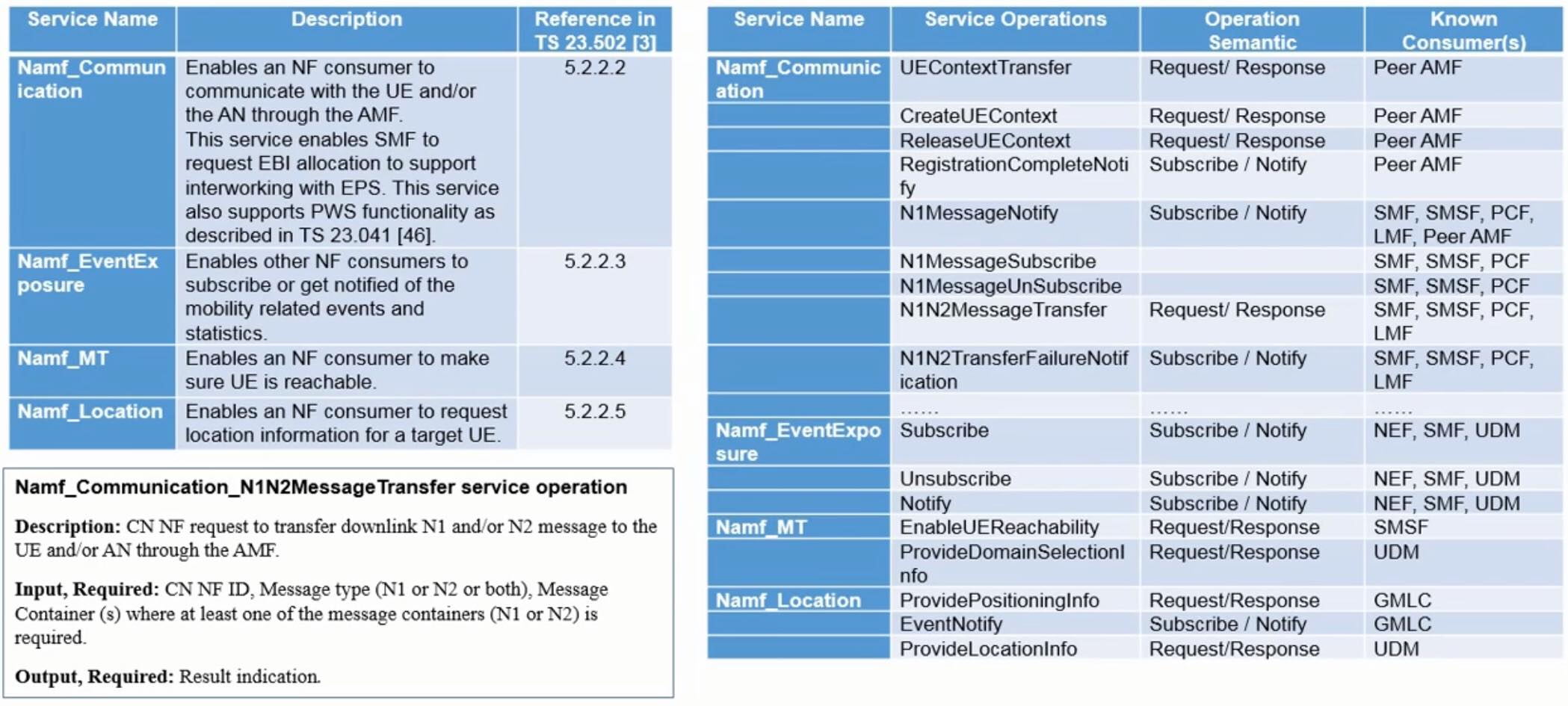
5G 核心网与 EPC 交互
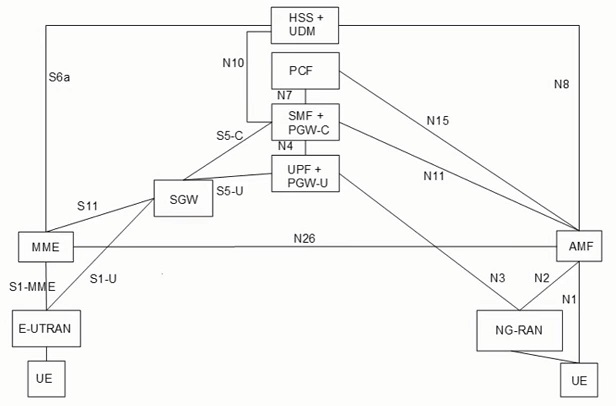
4G 网中的网元与 5G 中的 NF 若功能相似,可以联合部署
5G 系列文章
5G(一)5G 概述
5G(二)5G 网络架构 — 1. 核心网架构
5G(二)5G 网络架构 — 2. 接入网及网络部署
5G(三)5G 关键技术 — 1.NFV 网络功能虚拟化
5G(三)5G 关键技术 — 2.SDN 软件定义网络
5G(三)5G 关键技术 — 3.MEC 移动边缘计算
5G(三)5G 关键技术 — 4.Network Slicing 网络切片
5G(三)5G 关键技术 — 5.mmWave 毫米波
5G(三)5G 关键技术 — 6.Massive MIMO
5G(三)5G 关键技术 — 6.Massive MIMO 补充